BBX909 (moisture-curing type) and BBX-UV300 (UV-curing type) are available.
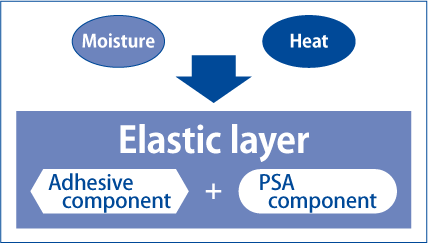
Mechanism of an elastic pressure-sensitive adhesive
Basic mechanism
This product has two key features: it is an adhesive that sticks firmly, and it is a pressure-sensitive adhesive that never solidifies. The product reacts to moisture contained in air (or UV radiation) to form a flexible, elastic film.
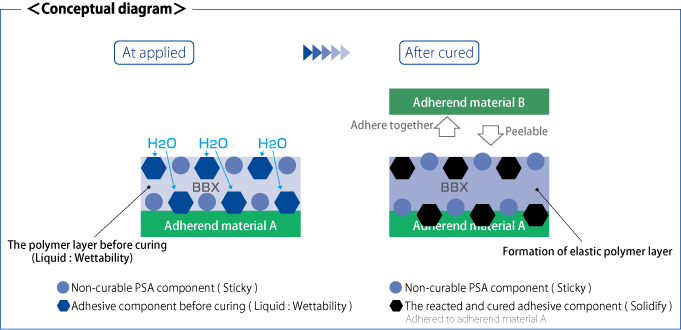
Secret to an easily peelable adhesive with minimal residue
As this pressure-sensitive adhesive is liquid, its “wetness” enables the surfaces to which it is applied to bond firmly, based on its adhesive property and tackiness property. The surface after open time exposure, however, bonds using the adhesive’s tackiness property only because the remaining adhesive property solidifies in reaction to the moisture (or UV radiation) contained within air. As a result, the adherend may be peeled from the tacky surface, which has a relatively smaller adhesion strength. In addition, since a resilient, highly stretchable elastic layer is formed, the adhesive may be peeled off neatly from the interface without cohesion failure. Although there are some exceptions, basically, BBX remains on the surface on which it was first applied.
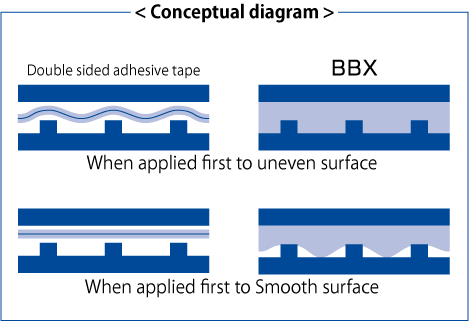
How BBX bonds slightly rough surfaces
As BBX is liquid, if you apply it onto a rough surface, it will spread over the uneven texture, securing an effective application area. However, if you apply the adhesive onto a smooth surface and then bond it to a rough surface after curing, BBX will not spread sufficiently over the uneven texture, compared to when the adhesive was in a liquid state, because the adhesive surface after the curing reaction turns into a semisolid tacky surface (like the surface of double-sided tape). Nevertheless, as BBX does not use a base material like that of a tape, and the pressure-sensitive adhesive forms a resilient layer, if you apply the adhesive thickly, you can expect to increase the effective contact area compared to that of tapes in general, achieving a greater sticking force.
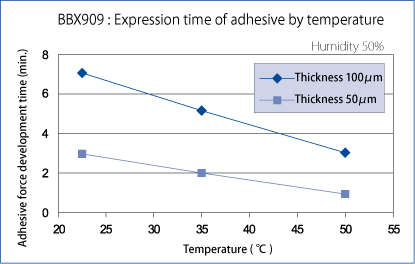
How to develop tackiness quicker
Basically, the tackiness can be developed quicker under these conditions: thin-film application, high temperature, and high humidity.
Adhesion performance data (JIS Z0237)
BBX909: Peel strength
(N/25mm)
| Adherends |
Peel strength |
| Silicone rubber |
18 |
| Natural rubber |
35 |
| SBR |
22 |
| Chloroprene rubber |
7 |
| Urethane rubber |
18 |
| EPDM |
11 |
| Leather |
18 |
The adhesive was applied to one side of the adherend, and then bonded to another adherend after 1 minute of open time.
Surface preparation: Treated using sandpaper, and degreased with solvent
Adhesive thickness: 100μm
Curing: 23°C 50%RH for 28 days after curing
Tension speed: 300 mm/min
BBX-UV300: Peel strength
(N/25mm)
| Adherends |
Peel strength |
| Stainless steel |
14.6 |
| Aluminum |
14.4 |
| Acrylic |
11.5 |
| Polycarbonate |
11.9 |
| Polystyrene |
15.2 |
| ABS |
15.4 |
| 6-Nylon |
14.2 |
| Hard vinyl chloride resin |
14.1 |
| Polyethylene |
5.5 |
| Polypropylene |
11.3 |
| Glass |
13.3 |
The adhesive was applied to the PET film at a thickness of 100 μm, then bonded to another adherend after UV radiation.
Lamp: Metal halide lamp
Cumulated amount of light: 3000mJ/cm2
BBX909: Tack development time
| Environmental condition |
Tack development time |
| 40°C 65%RH |
3 min |
| 23°C 50%RH |
7 min |
| 5°C 40%RH |
30 min |
Standard: Time required to achieve a 180º peel strength of 5 N/25 mm or greater.
BBX909: Changes in peel strength according to different open times
(N/25mm)
| Open time |
40°C 65%RH |
23°C 50%RH |
5°C 40%RH |
| Immediately following |
After 28 days |
Immediately following |
After 28 days |
Immediately following |
After 28 days |
| 3 min |
8 |
16 |
- |
15 |
- |
9 |
| 7 min |
12 |
19 |
6 |
17 |
- |
9 |
| 30 min |
19 |
21 |
7 |
20 |
6 |
9 |
| 120 min |
20 |
22 |
15 |
22 |
9 |
19 |
Adherends: PET film x Stainless steel
Adhesive thickness: 100 μm coating (single side on stainless steel side)
BBX909 tack property
| Open time condition |
Inclined ball tack |
| 23°C 50%RH |
30 min later |
17 |
| After 24 h |
22 |
BBX909 holding power
| Adherends |
Displacement |
| Stainless steel x PET film |
40°C |
0mm |
| 80°C |
0mm |
The adhesive was applied to one side of the PET film, then bonded to a stainless-steel adherend after 30 minutes of open time.
Adhesive thickness: 100 μm
Application area: 25mm x 25mm
Test method: The materials were left in an environment under each temperature for 60 minutes, under 1-kg load. The displaced distance, or the time until the PET film dropped was measured.
Stickiness of BBX909 to olefin resin
(N/25mm)
| Adherends |
PET side coating |
Applied to adherend |
| PE x PET film |
9 |
14 |
| PP x PET film |
12 |
10 |
The adhesive was applied to one side of the PET film, then bonded to a stainless-steel adherend after 30 minutes of open time.
The adhesive was applied to one side of the adherend, then bonded to PET film after 30 minutes of open time.
Adhesive thickness: 100 μm
Test method: JIS Z0237, 23°C50%RH 4 W curing
Product data
Property
| |
BBX909 |
BBX-UV300 |
| Application / Properties / Features |
Moisture curing type |
UV-curing type / RoHS-compliant |
| Type |
One-part elastic adhesive |
One-part UV curable elastic adhesive |
| Base |
Acrylic modified silicone resin |
Acryl |
| Appearance |
Light yellow transparent paste |
Light yellow clear liquid |
| Nonvolatiles |
wt% |
94 |
|
| Viscosity |
Pa・s/23°C |
26 |
55 |
| Density |
g/cm3 |
0.97 |
1.03 |
| Tack development time |
23°C |
7 min |
|
| Recommended cumulative amount of light *1 |
mJ/cm2 |
|
3000 |
| 180° degree peel strength |
N/25mm *2 |
20 |
|
| Adhesion properties |
Adhesive strength |
N/25mm *3 |
|
16.9 |
| Stickiness (PET film x Stainless steel) |
Ball No. *4 |
17 |
|
| Ball No. *5 |
22 |
|
| Holding power (PET film x Stainless steel) |
mm/1kg・80°C*6 |
0 |
0 |
| Cured properties |
Hardness |
Asker C |
|
27 |
| Breaking strength |
MPa |
|
0.2 |
| Elongation at break |
% |
|
1425 |
| Electric Characteristics |
Volume resistivity |
Ω・cm |
|
4.22 x 1012 |
| Surface resistivity |
Ω/sq |
|
3.89 x 1013 |
| Insulation breakdown voltage |
kV/mm |
|
15.1 |
| Dielectric constant |
100Hz |
|
5.62 |
| Dielectric loss tangent |
100Hz |
|
0.078 |
| |
|
 |
| Capacity |
135mL |
1kg |
